C++ 智能指针
C++指针支持使用 和 运算符动态分配和释放newdeletenewoperator newdeleteoperator delete
C++ 智能指针思路类似于在语言(如 C#)中创建对象的过程:创建对象后让系统负责在正确的时间将其删除。 不同之处在于,单独的垃圾回收器不在后台运行;按照标准 C++ 范围规则对内存进行管理,以使运行时环境更快速更有效。
实际的C++开发过程中存在程序崩溃、程序运行所需内存越来越多的问题等,主要原因有:
内存资源已经释放,但它的指针并没有改变指向(未指向nullptr,成为了野指针),并且后续还在使用。
有些内存资源已经释放,后期又试图再次释放(重复释放会导致程序运行崩溃)。
没有及时释放不再使用的内存资源,造成内存泄漏。
C++在 98/03 标准时支持使用 auto_ptr 智能指针来实现堆内存的自动回收,C++11标准在废弃 auto_ptr 同时添加了 unique_ptr,shared_ptr 以及 weak_ptr 3个智能指针来实现堆内存的自动回收。
C++ 智能指针底层是采用引用计数的方式实现的。简单的理解,智能指针在申请堆内存空间的同时,会为其配备一个整形值(初始值为 1),每当有新对象使用此堆内存时,该整形值 +1;反之,每当使用此堆内存的对象被释放时,该整形值减 1。当堆空间对应的整形值为 0 时,即表明不再有对象使用它,该堆空间就会被释放掉。
share_ptr 初始化 智能指针类模板 \ 头文件,并位于 std 命名空间中。
1 2 #include <memory> using namespace std ;
unique_dir、weak_ptr 指针不同之处:多个 shared_ptr 智能指针可以共同使用同一块堆内存。
构造 shared_ptr\ 类型空智能指针
1 2 3 4 std ::shared_ptr <int > p1; std ::shared_ptr <int > p2 (nullptr ) std ::shared_ptr <int > p3 (new int (10 )) std ::shared_ptr <int > p3 = std ::make_shared<int >(10 );
shared_ptr 模板还提供有相应的拷贝构造函数和移动构造函数:
1 2 3 4 std ::shared_ptr <int > p4 (p3) std ::shared_ptr <int > p5 (std ::move (p4))
p3为左值,调用拷贝构造函数
使用std::move(p4)来说,函数会强制将p4转换成对应的右值,且 std::move(p4)初始化p5,使得p5拥有了p4的堆内存,而p4变成了空智能指针。
注意:同一普通指针不能同时为多个 shared_ptr 对象赋值,否则会导致程序发生异常
1 2 3 int * ptr = new int ;std ::shared_ptr <int > p1 (ptr) std ::shared_ptr <int > p2 (ptr)
内存释放(自定义) shared_ptr 指针默认的释放规则不支持释放数组,只能自定应双方规则。
C++11 标准中提供的 default_delete\ 模板类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 std ::shared_ptr <int > p (new int [10 ], std ::default_delete<int []>() ) void deleteInt (int *p) delete []p; } std ::shared_ptr <int > p (new int [10 ], deleteInt)
借助 lambda 表达式进行初始化:
1 std ::shared_ptr <int > p (new int [10 ], [](int *p) { delete []p; } )
std::shared_ptr 可以通过 get()方法来获取原始指针,通过 reset() 来减少一个引用计数,通过 use_count()来查看一个对象的引用计数。
也就是说 子引用reset时父引用也会减1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 auto pointer = std ::shared_ptr <int >(10 );auto pointer2 = pointer; auto pointer3 = pointer; int *p = pointer.get (); std ::cout << "pointer.use_count() = " << pointer.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << pointer2.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer3.use_count() = " << pointer3.use_count() << std ::endl ; pointer2.reset(); std ::cout << "reset pointer2:" << std ::endl ;std ::cout << "pointer.use_count() = " << pointer.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << pointer2.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer3.use_count() = " << pointer3.use_count() << std ::endl ; pointer3.reset(); std ::cout << "reset pointer3:" << std ::endl ;std ::cout << "pointer.use_count() = " << pointer.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << pointer2.use_count() << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "pointer3.use_count() = " << pointer3.use_count() << std ::endl ;
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void bar (std ::unique_ptr (Entity) e) } void foo () auto e = std ::make_unique<Entity>(); e->doSomething(); bar(std ::move (e)); } foo();
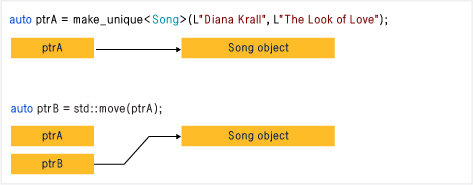
std::unique_ptr std::unique_ptr 是一种独占的智能指针,它禁止其他智能指针与其共享同一个对象。如:
1 2 std ::unique_ptr <int > pointer = std ::make_unique<int >(10 ); std ::unique_ptr pointer2 = pointer;
std::unique_ptr 只能使用 move 函数进行移动。
std::unique_ptr 不能直接进行函数传参,只能通过foo(std::move(p)) 方式传递。
使用 unique_ptr 进行封装指向大型对象的指针:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class LargeObject { public : void DoSomething () }; void ProcessLargeObject (const LargeObject& lo) void SmartPointerDemo () std ::unique_ptr <LargeObject> pLarge (new LargeObject()) pLarge->DoSomething(); ProcessLargeObject(*pLarge); }
或者使用reset来进行手动释放指针:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void SmartPointerDemo2 () std ::unique_ptr <LargeObject> pLarge (new LargeObject()) pLarge->DoSomething(); pLarge.reset(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std ;struct Fun { fun(){std ::cout <<"Fun::fun()" << endl ;} ~fun(){std ::cout <<"Fun::fun()" << endl ;} void fun () std ::cout <<"Fun::fun" << endl ;} } void f (const Fun &) std ::cout <<"f(const Fun&)" <<std ::endl ; } void main () std ::unique_ptr (Fun) p (std ::make_unique<Fun>() ); if (p) p->fun(); std ::unique_ptr <Fun) p1 (std ::move (p)); f(*p); if (p1) p1->foo(); if (p) p->foo(); p = std ::move (p1); if (p1) p1->foo(); std ::cout << "p1 被销毁" << std ::endl ; } if (p) p->foo(); }
std::weak_ptr weak_ptr 使用之前必须转换为 shared_ptr
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 void observe (std ::weak_ptr<Entity> ew) if (std ::shared_ptr <Entity> p = ew.lock()){ std ::cout <<p.use_count()<<std ::endl ; std ::cout <<"entity still alive." <<std ::endl ; }else { std ::cout <<"entity was expired." <<std ::endl ; } } void ex () puts ("-------------" ); puts ("enter" ); std ::weak_ptr<Entity> ew; { puts ("enter scope" ); auto e1 = std ::make_shared<Entity>(); std ::cout <<e1.use_count()<<std ::endl ; ew = e1; std ::cout <<e1.use_count()<<std ::endl ; observe(ew); puts ("leave scope" ); } observe(ew); puts ("leave" ); } enter; enter scope; entity create; 1 ;1 ;2 ;entity still alive; leave scope; entity was destroyed; leave;
std::shared_ptr 在类间指针类型的成员变量互相引用的情况下会出现无法释放的问题:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 struct A ;struct B ;struct A { std ::shared_ptr <B> pointer; ~A(){ std ::cout <<"delete A" <<std ::endl ; } } struct B { std ::shared_ptr <A> pointer; ~B(){ std ::cout <<"delete B" <<std ::endl ; } }
使用 std::weak_ptr 弱引用,弱引用不会引起引用计数的增加。
std::weak_ptr 没有 * 和 -> 运算符,不能够对资源进行操作。
它可以用来检查 std::shared_ptr 是否存在,expired() 方法能够检测资源未释放时返回false,释放时返回true。
还可以用来获取指向原始对象的 std::shared_ptr ,其lock() 方法在原始对象未被释放时,返回一个指向原始对象的 std::share_ptr 指针,进而访问原始对象的资源,否则返回 nullptr。
智能指针类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 template <class T >class SharedPointer { public : SharedPointer() :m_refCount(nullptr ), m_pointer(nullptr ){} SharedPointer(T* adoptTarget) :m_refCount(nullptr ), m_pointer(adoptTarget) { addReference(); } SharedPointer(const SharedPointer<T>& copy) :m_refCount(copy.m_refCount), m_pointer(copy.m_pointer) { addReference(); } virtual ~SharedPointer() { removeReference(); } SharedPointer<T>& operator =(const SharedPointer<T>& that) { } bool operator ==(const SharedPointer<T>& other) { } bool operator !=(const SharedPointer<T>& other) { } T& operator *() const { } T* operator ->() const { } int GetReferenceCount() const { } protected : void addReference() { } void removeReference() { } private : int * m_refCount; T * m_pointer; };